Human resources are a crucial asset for every form of business. But, it is the toughest to maintain. In recent times, the attrition rate has increased in several industries. There are multiple reasons, one of which is a lack of training and development. Do you know how it impacts the business?
For instance, a report suggests that by 2030, it is estimated that 85 million jobs will go unfilled due to a lack of available skills. Therefore, the profits will dip by a large margin. As we all know, business runs on profit, and to make more of it, you need “the right people at the right place.”
However, “the right people with the necessary skill set” allows the organization to grow at the market pace.
IT industry leaders understood this, and they started offering value addition courses and training and development programs for their existing employees. Still, the vacant seats in several companies reveal how they have not been able to achieve their desired results.
This blog is a comprehensive guide to Training and Development (T&D) in HRM (Human Resource Management). It comprises the below-mentioned information:
What is training and development in HRM?
Training and Development programs refer to the process of acquiring knowledge, skills, and attitudes that help improve employees’ job performance and enable future career growth.
Training employees is a formal process by which talent development professionals help individuals improve their performance at work.Usually, the goal is to enable employees to improve in their current roles in the short term.
Development pertains to the sustained advancement of a person’s professional life. Developing new abilities, mindsets, or knowledge is what gets people ready for new roles or responsibilities. Participating in conferences, work shadowing, mentorship, and continuing education are examples of development activities.
Understanding the Importance of Training and Development in HRM
- Improved Productivity: Staff training is directly linked to better performance because it helps employees become more skilled, confident, and knowledgeable about their industry. Organizations may enhance employee efficiency, productivity, and job satisfaction by providing employees with the required training and resources.
- Efficient Risk Management: Employees with proper training are less likely to make costly mistakes or run afoul of the law. Compliance training, for example, can help businesses stay out of trouble with the law by making sure staff members are aware of the rules that affect the work they do on a daily basis.
- Ensure Employee Satisfaction: Employees are more engaged and motivated in their work when they perceive that their organization is dedicated to their professional development and advancement. To guarantee that the knowledge acquired can be quickly implemented in the workplace, the program must be customized to the unique needs of the personnel. Only then can it be considered effective.
- Cultivating Self-Motivated Employees:Attending in-depth training and development courses equips staff members to deal with obstacles at work on their own. It further reduces their reliance on constant supervision and guidance. This self-motivation cultivated through training enhances individual and team performance, contributing to a more efficient and self-sufficient workforce.
- Enhancing Organizational Productivity: An organization’s productivity heavily relies on the skill set of its employees. Employees can keep up to date and learn new skills through training and development programs. Thereby positively impacting the organization’s productivity.
Types of Training and Development

- Technical skill development: Depending on the type of job, technical training will be required. Technical training is based on a technical product or task.
Assume your business has decided to migrate to the most recent Microsoft Office version. To guarantee that everyone uses the technology efficiently, the entire firm might have to take some technical training.
- Leadership Development: Any activity that improves a person’s or an organization’s capacity for leadership is referred to as leadership development. To build the knowledge and abilities needed to lead, it consists of exercises including work rotation, mentoring, coaching, learning events, self-study, and special assignments.
- Soft skill development: Soft skills refer to personality traits, social graces, communication, and personal habits that characterize relationships with other people. These skills enable a person to work professionally, collaborate with colleagues without major disagreements, and contribute to a coordinated team effort.
- Compliance training: Compliance training is often industry-specific but may include topics such as cybersecurity and sexual harassment. These training initiatives are mandatory, so logically, the focus is on recording completion.
Effective corporate compliance initiatives support sound governance and the prevention of bad behavior inside your company.
- Executive development: This type aims to give non-executive staff members the tools they need to advance into leadership roles. It is intended for those who are already in a leadership position within their company.
Employers can ascertain whether a candidate has the capacity to become a leader by doing executive development exercises.
- Safety training focuses on improving organizational health and safety and reducing workplace injuries. It can encompass employee, workplace, customer, and digital and information safety. Safety training includes both training that is required by law and training that organizations offer without legally being required to do so.
- Management development: It focuses on providing managers with the knowledge and skills that they need to be effective managers and developers of talent. Accountability, cooperation, communication, engagement, listening, and assessment are a few possible topics.
Furthermore, it also helps those who are new to management positions understand what the job entails and gain the necessary soft skills and interpersonal knowledge.
What are the 5 processes of Training and Development?

A well-designed process is much more efficient in creating and executing a suitable training and development plan.
The following are the preferred five processes of training and development in HRM:
1. Needs Assessment
The first process involves identifying the organization’s skill gaps and determining the training needs of employees. It comprises gathering data through surveys, focus groups, or other assessment tools to identify areas that need additional training or development. Establishing training and development objectives that complement the organization’s overarching plan is essential.
2. Design and Development
The design of the training program to address recognized needs and match them with the strategic goals of the organization is the focus of the second process. Creating training materials, choosing suitable training techniques, designing a training schedule, and setting learning objectives are all part of the design process. The training program focuses on understanding individual learning styles and preferences and customizing them to meet specific needs.
3. Delivery
This third process comprises implementing training programs through various training methods like classroom training, online training, on-the-job training, and coaching. It needs to concentrate on the accessibility of resources, the proper size of the workforce, and the unique learning preferences of each employee. Employee engagement and learning results are improved when training programs are delivered effectively.
4. Evaluation
It is the fourth process and usually evaluates the effectiveness of the training program. Surveys, assessments, performance indicators, and focus groups are some of the possible methods. It draws attention to the areas that need work. Businesses may measure the performance of their training programs and make future adjustments with the aid of an efficient evaluation procedure.
5. Follow-Up
Confirming the training concepts and their useful implementation in day-to-day work constitutes the last step in the training and development process. It consists of feedback meetings, refresher training, and continuous coaching to track development and make sure the company is meeting goals. Effective follow-up aids in the retention of acquired knowledge and skills by employees as well as their practical implementation.
Challenges in Training and Development
1. Identifying the Best Training Method
When choosing the finest kind of training approach for employee training programs, resources aren’t the only factor to take into account. Organizations also need to pay attention to the specific needs of their employees. There are a variety of training methods available including on-the-job training, in-person training, and online learning or e-learning and everyone responds differently depending on their learning style.
Employers must take the time to examine and evaluate the various training options available. In addition, they must consult with staff members to ascertain the most effective learning style.
2. Determining Training Needs
Organizations must ascertain the precise competencies and expertise that staff members require to carry out their tasks as effectively as possible before putting in place any type of training program. The training program needs to address both the learner’s needs and the organization’s needs as a whole. A lack of assessment of the organization’s and the individual’s needs can result in inefficient training and resource waste.
To overcome this challenge, organizations need to gain a clear understanding of what competencies are required for each role and align these to their employee’s skill gaps
3. Allocating Resources
To ensure a high-quality training experience, organizations need to allocate the necessary resources. Development program design and delivery can be expensive, therefore businesses must make strategic planning decisions to strike a balance between the necessary resources and training quality. With little funding, small and medium-sized businesses may find this particularly difficult.
Organizations must evaluate the many training delivery options available and prioritize their training goals in order to overcome this obstacle. Instead of pursuing in-person training, cost-effective methods of delivering training frequently involve outsourcing program components or making use of technology and online learning platforms like Coursera.
4. Measuring the Impact of Training
For businesses, quantifying the advantages of a training program and explicitly connecting it to business goals can be a major difficulty when measuring the impact of training. It’s important to measure the impact of training as it enables organizations to better demonstrate the value to stakeholders and make data-driven decisions to adjust programs where necessary.
Using targets that are Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant, and Timely (SMART) helps identify desirable outcomes. After that, organizations should use metrics and statistics to monitor development and assess the effectiveness of their initiatives. Success can be measured in some ways, including the level of engagement and satisfaction among staff members, how well individuals and teams perform following training, and the influence on the bottom line and corporate objectives.
5. Keeping Employees Engaged
Most people agree that one of the main difficulties with corporate training is engagement. Employees may find it challenging to begin or finish their training due to juggling everyday obligations, hectic schedules, and conflicting priorities. When a training program doesn’t interest them or suit their preferred method of learning, learners also lose interest in it.
Employers should consider setting out a certain period of an employee’s day or week for training to help with employee retention. This guarantees that employees have adequate time to commit to upskilling and don’t feel pressured to balance their duties. Organizations need to locate educational materials that draw people’s interests.
How do you measure Employee Performance after Training?
The effectiveness of the training program and the use of newly acquired skills and information by employees must be assessed through post-training performance evaluations. Here are a few methods for measuring post-training employee performance:
- 360-Degree Reviews
Collecting feedback from a wide range of stakeholders, like managers, HR, and subordinates. It presents a comprehensive picture of employee efficiency and identifies areas in need of development. Furthermore, it helps gather information on how employees apply their skills and knowledge and identify areas where the employees excel and need additional support.
Incorporating feedback in future training programs helps organizations support the employees’ ongoing development. Regular check-ins with employees can also help employees apply the skills and knowledge learned in their everyday work.
Create a culture of continuous learning and improvement to ensure that organizations are consistently meeting the needs of their employees.
- Continuous Feedback
Giving staff guidance and feedback is a continuous activity. It typically entails establishing precise performance standards and giving frequent updates on the status of these objectives.
Following training, managers can keep an eye on how well staff members are applying the knowledge and skills they have learned in the real world by giving them regular feedback. It greatly aids workers in making adjustments to their tasks in real time.
- OKRs
The acronym OKRs stands for Objectives and Key Results. To measure progress, they use both qualitative and quantitative measurements. The purpose of OKRs is to assess how training initiatives affect employee output. They offer a precise and quantifiable means of monitoring the effect of the training program on worker productivity.
For instance, if the training program was focused on improving customer service, the firm could set a goal to increase customer ratings by a certain percentage.
Examples of Companies with Training and Development Programs
Here are a few examples of training and development programs used by top brands:
- Amazon: To help employees enhance their skills in a variety of areas, including technology, leadership, and customer service, Amazon offers comprehensive on-the-job training. Furthermore, its exclusive Career Choice program covers 95% of employees’ tuition and expenses so they can pursue education and success in industries with high demand.
- Microsoft: Technical training, leadership development, and career development workshops are just a few of the many training and development initiatives that Microsoft permits. Employees can work together to discover fresh concepts and solutions during the company’s yearly hackathon event.
- Starbucks: Starbucks is well-known for the Starbucks Experience, a thorough staff training program. Training courses are offered both in-person and virtually as part of the curriculum; topics often include drink preparation, coffee expertise, and customer service. Managers give staff members ongoing coaching and feedback to help them perform better.
- Google: A variety of training and development initiatives, such as programs for employee wellbeing, technical skill development, and leadership development, are available to Google staff members. Employees can instruct and learn from one another in their areas of expertise thanks to a specially created program by the organization.
Current Trends in Training and Development
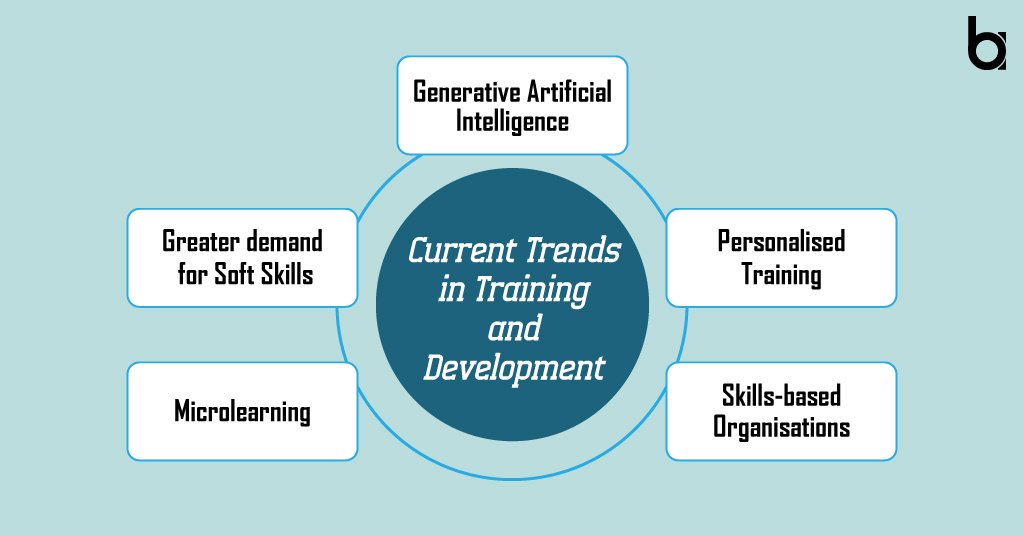
The workplace is constantly evolving, and so are the current training and development trends. Just to keep an eye on them, here is the list of the top 5 current trends in training and development that enterprises use to upskill the workforce:
1. Generative Artificial Intelligence
Incorporating AI in training and development would mean more automation and personalization. Additionally, resources and training programs specifically designed for each employee can be shared by an AI-based learning tool.
Grand View Research estimates that the entire amount spent on hardware, software, and services related to artificial intelligence (AI) was approximately $200 billion in the previous year. However, by 2030, that amount is predicted to grow by 820% to surpass $1.8 trillion.
2. Greater demand for Soft Skills
Professionals with strong critical, analytical, and effective communication abilities are in higher demand due to the availability of generative AI and the quick development of professional skills.
This suggests that the development of soft skills—now dubbed “power skills”—will receive more attention. According to a Deloitte poll, by 2030, soft skills will be heavily utilized in two-thirds of all occupational roles.
3. Microlearning
The need for microlearning is rising as companies become more mobile-focused.
It is designed for employees seeking to learn on-the-go and organizations seeking to provide just-in-time learning. It is primarily helpful for employees with busy schedules or working remotely, and this helps them learn at their own pace and time.
4. Personalised Training
Personalized training is a tailored approach to learning and development that addresses the specific needs and preferences of individual learners. Its programs are based on the employees’ current skills, knowledge, and learning needs.
In addition, it focuses on an individual employee’s strengths and weaknesses and aims to improve and overcome them.
5. Skills-based Organisations
Big businesses are moving away from positions requiring a high level of professional certification and toward a strategy that sees employment as a collection of talents. This change responds to the demand for more skill acquisition agility in a market that is changing at an ever-increasing rate.
Deloitte reports that 98% of business executives plan to incorporate more skills-based approaches in the future.
Conclusion
Training and development trends are reshaping the human resources environment for 2024 and beyond. Organizations are reinventing employee training due to the shift to skill-based practices, the growing importance of generative artificial intelligence, the need for “soft skills,” and microlearning.
Organizations must also be ready to invest in the growth of their workforce. This includes providing the greatest development plans along with roles that are clearly defined, sustainable workloads, and challenges that push team members to perform at their highest levels while preserving well-being and fostering a strong workplace culture.




















