The Budget Session 2022 has begun in the Indian Parliament. As 1 April 2022 marks the beginning of a new Financial year or a Fiscal year, several new rules are coming into effect. Amongst these latest rules is the introduction of the ‘Indian Antarctica Bill’. The Indian Union minister Jitendra Singh is all set to introduce the bill in the Lok Sabha for providing a regulatory framework for India’s research activities in the Antarctic.
The Indian Antarctic Bill
Piloted by the Ministry of Earth Sciences, the Indian Antarctica Bill is expected to help India fulfill its obligation under the following conventions:
- The Antarctic Treaty of 1959
- The Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources of 1982
- The Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty of 1998
On 17 March 2022, the Union Cabinet approved the draft legislation to provide a regulatory framework for India’s research activities in Antarctica and protect the environment in the icy continent. The Indian Antarctica Bill is a part of the Indian Antarctic programme which began in 1981.
The Indian Antarctic Programme
The Indian Antarctic Programme is a multi-disciplinary and multi-institutional programme, under the control of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India. Under the programme, atmospheric, biological, earth, chemical, and medical sciences are studied by India.
To simplify, the Indian Antarctic Programme has completed 40 scientific expeditions to date. Moreover, three permanent base stations were built by India in the Antarctic under the programme, namely—
- Dakshin Gangotri Antarctic research base (1983)
- Maitri base (1988)
- Bharati base (2012).
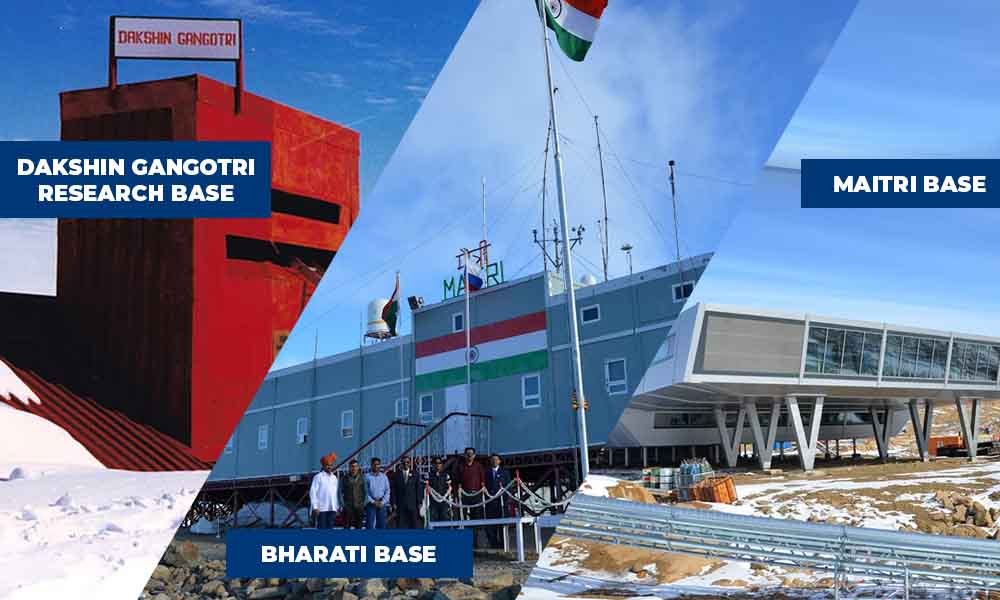

Currently, the Bharati and Maitri base are completely operational. Additionally, India plans to build another research facility to replace the Maitri base since it has outlived its life and structural integrity. The Indian Antarctic Programme is bound by the rules of the Antarctic Treaty System, which was signed by India in 1983.
The Antarctic Treaty System (1959)
In 1983, India became a part of the Antarctic Treaty System (ATS). Following is the detailed timeline of India’s partaking in the various international activities as a part of the ATS:
- 12 Sept 1983: India achieved the status of Consultative Party.
- 1 Oct 1983: Became a member of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR).
- 1986: Became a member of the Convention for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR).
- 1997: Ratified the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty and reaffirmed its commitment to protecting the Antarctic environment.
- 1999: Hosted the 11th COMNAP/SCALOP (Standing Committee on Antarctic Logistics and Operations) meeting in Goa.
- 1998: Hosted the and the working group meeting on eco-system monitoring and management of CCAMLR and occupied the Chair from November 1998 for 2 years.
Why the Antarctic?
Antarctica is defined as all the land and ice shelves south of 60°S latitude. ATS was the first arms control agreement established during the Cold War. It distinguished the continent as a scientific preserve, establishing freedom of scientific investigation, and banning military activity; for the purposes of the treaty system.
The Antarctic is the single continent where no human inhabitation is found. The icy region holds utmost scientific significance. Numerous global project researchers cite the Antarctic as the origin of continents, climate change, meteorology as well as pollution. In addition, the ecosystem of the region has fascinated scientists and researchers for years.
Read more: When will India become an electronic hub?