The achievements of ISRO make every Indian proud of their pioneering journey in space exploration. But the foundation of this remarkable story began earlier in the 1960s era.
In 1962, the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) laid the groundwork for India’s space program. It set the stage for what would later become the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), officially founded in 1969. ISRO took on the ambitious goal of harnessing space technology for national development, transforming the dreams of a young nation into reality.
Since its inception, the achievements of ISRO have been nothing short of extraordinary. From launching satellites that revolutionize communication and remote sensing to mastering indigenous technologies like the cryogenic propulsion system, ISRO has not only advanced India’s space capabilities but also established itself as a global leader. Each mission has expanded the reach of science and technology, from agriculture and telecommunication to disaster management.
ISRO’s mission to harness space technology for the betterment of society continues to drive its innovations. The agency’s breakthroughs extend beyond cutting-edge technology, inspiring future generations through collaborations with academic institutions and initiatives that promote space research. As ISRO forges ahead, its achievements shape the future of space exploration both in India and on the global stage.
Here is the list of 10 Achievements of ISRO:
| Mission/Project | Year |
| Chandrayan 3 | 2023 |
| Aditya L1 | 2023 |
| Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) | 2023 |
| Mission Shakti (Anti-Satellite Missile) | 2019 |
| Launching 104 Satellites | 2017 |
| NavIC | 2016 |
| Mars Orbit Mission | 2014 |
| Chandrayan 1 | 2008 |
| Aryabhatta Satellite | 1975 |
| Vikas Engine | 1970 |
1. Chandrayaan 3-2023
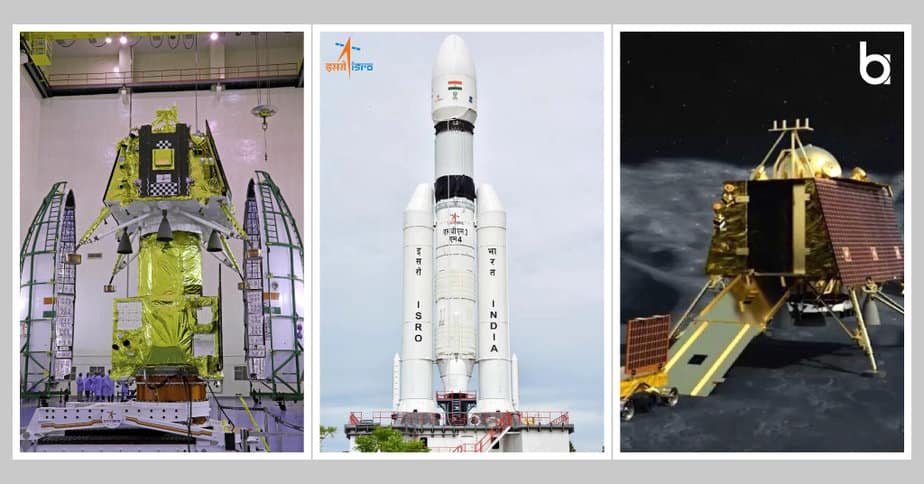

Chandrayaan-3 achieved a historic milestone by successfully landing on the Moon’s south pole on August 23, 2023. This mission aims to demonstrate advanced capabilities in soft landing and exploration of the lunar surface. It follows the earlier missions, Chandrayaan-1 and Chandrayaan-2, incorporating valuable lessons learned from past experiences. In recognition of this achievement, ISRO chairman S. Somanath received the prestigious IAF World Space Award for Chandrayaan-3 on October 14, 2024, during a ceremony held in Milan, Italy.
- The lander successfully touched down near the lunar south pole on August 23 at 18:03 IST (12:33 UTC), making India the fourth country to achieve a soft landing on the Moon. Furthermore, at 69°S, it was the southernmost lunar landing until IM-1 landed further south in February 2024, marking one of the top achievements of ISRO.
- The six-wheeled Pragyan rover deployed from the lander and began exploring the lunar surface on August 24. However, on August 30, the rover confirmed the presence of sulfur on the Moon using the LIBS technique.
- Chandrayaan-3 made India the first country to land near the lunar south pole, a region that remains unexplored by other space agencies.
- Remarkably, this ambitious mission operates within a budget of approximately 615 crores, a testament to ISRO’s efficient resource management and strategic allocation of funds, further adding to ISRO’s latest achievements.
2. Aditya-L1 – 2023

The Aditya-L1 mission, launched on September 2, 2023, is India’s inaugural solar observatory designed to study various solar phenomena from Lagrange Point 1 (L1), situated approximately 1.5 million km from Earth. This strategic location allows for continuous solar observation without interruptions from eclipses or occultations.
- The mission is equipped with seven payloads, including a coronagraph for studying the solar corona and instruments for analyzing solar winds and magnetic fields.
- Aditya-L1 aims to explore critical questions regarding solar activities, such as coronal heating and the dynamics of space weather.
- The spacecraft is expected to operate for about five years, providing invaluable data to enhance our understanding of solar dynamics and their impact on Earth.
- The Supra Thermal and Energetic Particle Spectrometer (STEPS), part of the Aditya Solar Wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX), started collecting data on September 10, 2023. It measures supra-thermal and energetic ions and electrons, providing insights into the particle environment surrounding Earth.
3. Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) – 2023

The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a new class of launch vehicle developed by ISRO, designed to cater to the growing demand for launching small satellites. The SSLV had its inaugural flight in February 2023, marking a significant step in ISRO’s efforts to expand its launch capabilities. The uniqueness of its payload capacity makes it rank among the top achievements of ISRO.
- The Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) is a versatile launch vehicle developed by ISRO, capable of delivering payloads weighing up to 500 kg to low Earth orbit (LEO) and 300 kg to Sun-synchronous orbit.
- The SSLV features a three-stage design with solid-propellant-based engines, complemented by a fourth stage known as the Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) for precise orbital insertion.
- One of its standout characteristics is low-cost launch capabilities, with an expected cost of approximately ₹35 crore (about $4.2 million).
- The SSLV was successfully launched on February 10, 2023, deploying three satellites, including EOS-07, demonstrating ISRO’s commitment to cater to the growing demand for small satellite launches globally.
4. Mission Shakti (Anti-Satellite Missile) – 2019

Mission Shakti, conducted on March 27, 2019, signifies India’s successful anti-satellite (ASAT) missile test, positioning the nation as the fourth globally to demonstrate such capability. This mission has created a space for ISRO in the international space sector. Hence, it holds a special place among the achievements of ISRO.
- The test involved the targeted destruction of a live satellite located in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), utilizing indigenous technology adapted from India’s ballistic missile defense system.
- The successful completion of Mission Shakti is a testament to India’s growing space capabilities and strategic defense initiatives, instilling a sense of deterrence against potential threats.
- Notably, the operation was executed with minimal space debris generation, emphasizing ISRO’s commitment to responsible space practices.
5. Launching 104 Satellites – 2017

Among the numerous successes of ISRO, the first one we have on our list of the Top Achievements of ISRO is successfully launching 104 satellites with a single rocket. In 2017, they reached this milestone in partnership with six nations, employing the powerful PS: V-C37 and showcasing its remarkable capability in a single mission, achieving a significant milestone in the field of space exploration.
- ISRO’s achievements have been widely recognized, and one of the standout moments was their successful launch of an amazing 31 satellites simultaneously, demonstrating their worldwide reach. Notable countries such as the United Kingdom, the United States, and Germany entrusted ISRO with their satellites. This historic event took place on February 15, 2017.
- Its Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) outperformed the competition, transporting and delivering 104 satellites into sun-synchronous orbits in a single flight. This remarkable effort broke the previous record of 37 satellites launched on June 19, 2014, by a Russian Dnepr rocket.
- On February 15, 2017, the 714-kilogram Cartosat-2 Series satellite, accompanied by 103 co-passenger spacecraft, was the central attraction of the show.
- PSLV-C37’s 104 satellites weighed a whopping 1378 kg in total. With this incredible achievement, the number of Indian satellites launched by PSLV has risen to 46.
6. NavIC – 2016

Creating India’s independent navigation system was one of the best achievements of ISRO. NavIC, or Navigation with Indian Constellation, is India’s regional satellite navigation system developed by ISRO, officially operational since 2016. The system consists of seven satellites, providing accurate positioning and timing information.
- Initially launched as the Indian Regional Navigational Satellite System (IRNSS), NavIC boasts a coverage area extending up to 1,500 km beyond India’s borders, making it essential for national security and independent navigation solutions.
- NavIC offers two primary services: a Standard Positioning Service (SPS) for civilian use and a Restricted Service (RS) for authorized users, enhancing its application across various sectors including transportation, agriculture, and disaster management.
- The system aims to position India as a self-reliant player in the global navigation landscape, reducing dependency on foreign systems like GPS.
7. Mars Orbit Mission – 2014

ISRO launched MOM in 2013, rightly named Mangalyaan, to expand the bounds of exploration by venturing into unknown territory, enabling humanity to unravel the secrets of the cosmos.
- The historic endeavor has caught the world’s attention, focusing clearly on understanding Martian terrain, morphology, minerals, and atmosphere. MOM, blasted into space by the powerful PSLV-XL, set out on its voyage to Mars.
- Since it first arrived at Mars on September 24, 2014, MOM has been in orbit around the planet. Its strategic orientation lets it gather detailed photographs of a whole Martian hemisphere simultaneously, thanks to a highly elliptical orbit spanning 423 80,000 km.
- MOM carries a color camera, a thermal infrared sensor, an ultraviolet spectrometer, a mass spectrometer, and a methane sensor, among other instruments that allow scientists to examine the Martian exosphere and investigate the existence of methane.
- Notably, on October 19, 2014, MOM had the unusual opportunity to view Comet Siding Spring as it gently glided by Mars, approaching 132,000 miles from the planet.
8. Chandrayan 1 – 2008

ISRO launched India’s first lunar exploration mission, Chandrayaan-1, which is one of the top achievements of ISRO. It successfully orbited the moon and made significant discoveries, contributing to our understanding of the lunar surface.
- In October 2008, ISRO launched this ground-breaking mission. It performed successfully from launch to August 2009, leaving a lasting legacy on space exploration.
- Chandrayaan-1 set out on an incredible journey, armed with a lunar orbiter and an impactor. In 2008, India reached new heights by launching the groundbreaking Chandrayaan project, the first-ever space journey to the moon.
- On October 22, 2008, a Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle launched into space the 590-kg (1,300-pound) Chandrayaan-1. The probe quickly rose into an elliptical polar orbit around the Moon, reaching an incredible altitude of 504 km (312 miles) at its closest approach to the lunar surface and a stunning 7,502 km (4,651 miles) at its farthest point.
- Following a thorough assessment, the spacecraft sank elegantly to a precise 100-kilometer (60-mile) orbit. On November 14, 2008, Chandrayaan-1 launched the Moon Impact Probe (MIP), a small but powerful craft revealing the existence of minuscule amounts of water in the Moon’s atmosphere.
9. Aryabhatta Satellite – 1975
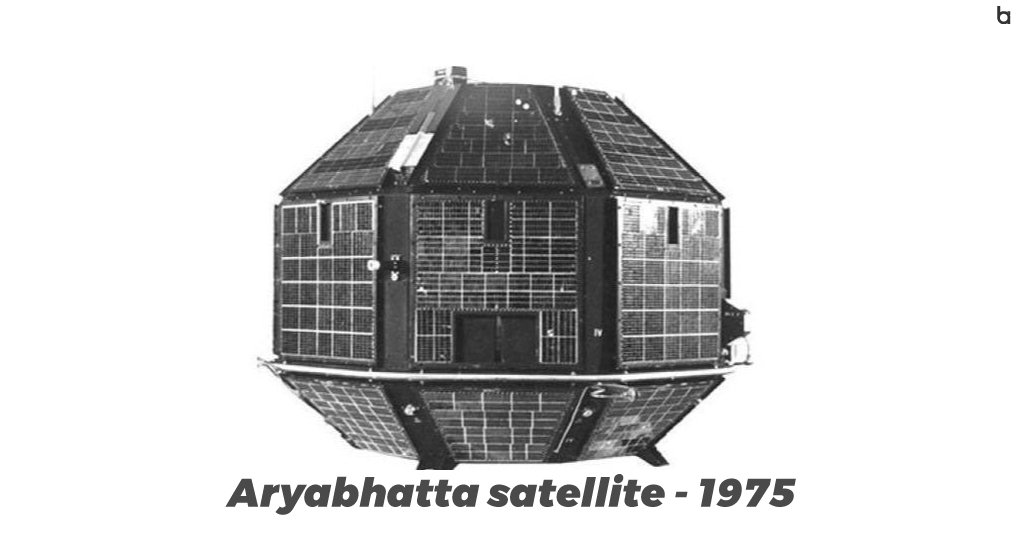
The Aryabhatta satellite, named after the ancient Indian mathematician, was launched into space. It played a significant role in advancing India’s space program and conducting scientific experiments.
- Aryabhata was launched into space on April 19, 1997. It was named after the great Indian astronomer and was built entirely in India. This ground-breaking satellite enthralled the world.
- Aryabhata was sent into orbit by the powerful Kosmos-3M launch vehicle from Kapustin Yar, a well-known Soviet rocket launch complex in Astrakhan Oblast. It embarked on a journey to unravel the mysteries of our planet and beyond with precision and grace.
- Aryabhata weighed 794 pounds (360 kg) and was outfitted with innovative technology. Its aim is to probe deep into the Earth’s ionosphere, meticulously analyzing the interesting neutrons and gamma rays emitted by our bright sun. Aryabhata was also programmed to discover the secrets of the universe through enthralling X-ray astronomy experiments.
- On the historic day of April 19, 1975, Aryabhata took flight, riding atop a Russian-made rocket within the Soviet Union’s borders. Aryabhata exemplifies India’s capability in space exploration.
10. Vikas Engine – 1970
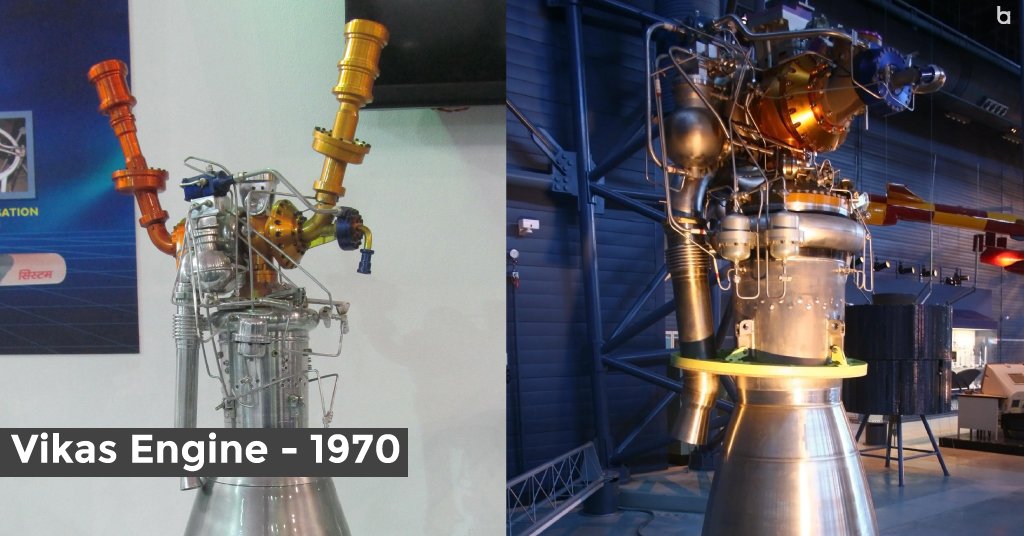
Lastly on our list of the Top Achievements of ISRO is the Vikas Engine. This powerful and reliable liquid rocket engine, developed by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), has played a significant role in the achievements of India in space. It has been extensively used in various launch vehicles, including the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV). The success of the Vikas Engine laid the solid foundation for India’s future achievements in space.
- The series of liquid-fueled rocket engines developed by ISRO scientists have redefined the possibilities for space exploration. A brilliant team at the Liquid Propulsion Systems Center, led by the extraordinary Nambi Narayanan, developed the Vikas engine in the 1970s.
- This marvel of Indian engineering has risen to tremendous heights by drawing inspiration from the licensed version of the Viking engine and combining it with an innovative chemical pressurization system.
- It also powers the PSLV’s second stage, boosts the performance of the GSLV Mark I and II, and serves as the fearsome core stage of the GSLV Mark III. This remarkable engine has carried missions such as Chandrayan and Mangalyaan to the stars.
- On January 30, 2023, ISRO reached a watershed moment: the Vikas engine’s initial throttling trial hot test was a success. Witness the engineering marvel’s accuracy and refinement as ISRO achieved a historic 67% power reduction for a stunning 43 seconds.
To add more, here’s a list of the Successful Missions of ISRO (Decade by Decade)
To truly appreciate the achievements of ISRO, let’s take a closer look at the launch statistics of different rockets over the decades. These tables show how well each rocket has performed in terms of successful launches, partial successes, and failures. Each rocket tells a story of growth and determination in India’s space journey.
Decade-wise Summary of PSLV Launches:
| Decade | Successful | Partial Success | Failure | Total |
| 1990 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 |
| 2000 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| 2010 | 33 | 0 | 1 | 34 |
| 2020 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Total | 57 | 1 | 2 | 60 |
Decade-wise Summary of GSLV Launches:
| Decade | Successful | Partial Success | Failure | Total |
| 2000 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 5 |
| 2010 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 8 |
| 2020 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
| Total | 10 | 2 | 4 | 16 |
Decade-wise Summary of LVM3 Launches:
| Decade | Successful | Partial Success | Failure | Total |
| 2010 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 2020 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Total | 7 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
Decade-wise Summary of SSLV Launches:
| Decade | Successful | Partial Success | Failure | Total |
| 2020 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
Landing off on Achievements of ISRO
These achievements of ISRO missions are milestones for Indian space exploration. Additionally, it is also pivotal for scientific research, national security, and technological advancement, reflecting India’s aspirations in the global space arena.
We hope that our blog on the top achievements of ISRO has provided you with valuable insights into the incredible accomplishments of this renowned space agency. To stay informed about other exciting topics, we encourage you to continue reading our blogs, where we strive to deliver valuable and engaging information on a wide range of subjects.
FAQs
What is the major achievement of ISRO?
ISRO’s major achievement is the successful landing of the Chandrayaan-3 mission on the Moon’s south pole on August 23, 2023. This milestone made India the first country to achieve a soft landing in this region and the fourth country globally to land on the Moon.
What is India’s latest achievement in space?
India’s latest achievement in space is the recognition of ISRO with the IAF World Space Award for the Chandrayaan-3 mission, awarded on October 14, 2024. This award highlights the mission’s significant contribution to lunar exploration.
What are the important points of ISRO history?
- Formation: ISRO was established on August 15, 1969.
- First Satellite: Aryabhata, India’s first satellite, was launched on April 19, 1975.
- Chandrayaan-1: Launched in 2008, this mission discovered water on the Moon.
- Mars Orbiter Mission: In 2013, Mangalyaan made India the first country to reach Mars on its first attempt.
- Chandrayaan-3: Launched on July 14, 2023, it successfully landed on the Moon on August 23, 2023.
What is an amazing fact about ISRO?
An interesting fact about ISRO is that it launched a record 104 satellites in a single mission in 2017, demonstrating India’s capability in small satellite launches. Additionally, ISRO conducts these missions at a fraction of the cost of similar programs, showcasing its efficiency and ingenuity.
How many successful missions of ISRO?
As of now, ISRO has successfully completed a total of 124 spacecraft missions and 94 launch missions, solidifying its position as one of the leading space organizations in the world.
What was the first successful launch of ISRO?
ISRO’s first successful launch occurred in 1980 with the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV-3), which successfully placed the Rohini satellite into orbit, making India the seventh country in the world to achieve this capability.
ALSO READ: The Invention of Telescope: Beginning of a New Era in Space Research